Building Scalable Applications with Django and Next.js: A Full-Stack Guide
Introduction:
As a Senior Full Stack Engineer and Product Lead at Zettaworks Technologies, I’ve had the opportunity to build scalable applications that solve real-world problems. One of my most notable projects is Qomuniti, a platform for estate safety and community engagement that achieved over 1,000 registered users and a 30% mobile app retention rate.
In this post, I’ll walk you through the process of building a scalable application using Django and Next.js, two powerful frameworks for backend and frontend development.

1. Why Django and Next.js?
Django: A Python-based framework that simplifies backend development with its built-in ORM, admin panel, and robust security features.
Next.js: A React-based framework that enables server-side rendering (SSR) and static site generation (SSG), making it ideal for building fast, SEO-friendly web applications
Together, these frameworks provide a solid foundation for building scalable, high-performance applications.
2. Setting Up the Backend with Django
Start by creating a Django project and setting up the necessary models, views, and APIs. For example, in Qomuniti, I used Django to:
Manage user authentication and authorization.
Handle data storage and retrieval for features like the Panic Button and e-wallet system.
Implement RESTful APIs using Django REST Framework (DRF).
Here’s a quick example of a Django model for a user profile:

pythonExecuteCopy Codefrom django.db import models
class UserProfile(models.Model):
user = models.OneToOneField(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
phone_number = models.CharField(max_length=15)
address = models.TextField()
def __str__(self):
return self.user.username
3. Building the Frontend with Next.js
Next.js makes it easy to create dynamic, responsive user interfaces. For Qomuniti, I used Next.js to:
Build interactive dashboards for users and admins.
Implement SSR for faster page loads and better SEO.
Integrate with the Django backend using Axios for API calls.
Here’s an example of a Next.js page that fetches data from the Django API:
javascriptCopy Codeimport axios from 'axios';
export async function getServerSideProps() {
const res = await axios.get('https://api.example.com/users');
return { props: { users: res.data } };
}
export default function Users({ users }) {
return (
<div>
<h1>User List</h1>
<ul>
{users.map(user => (
<li key={user.id}>{user.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
4. Deployment and Scaling
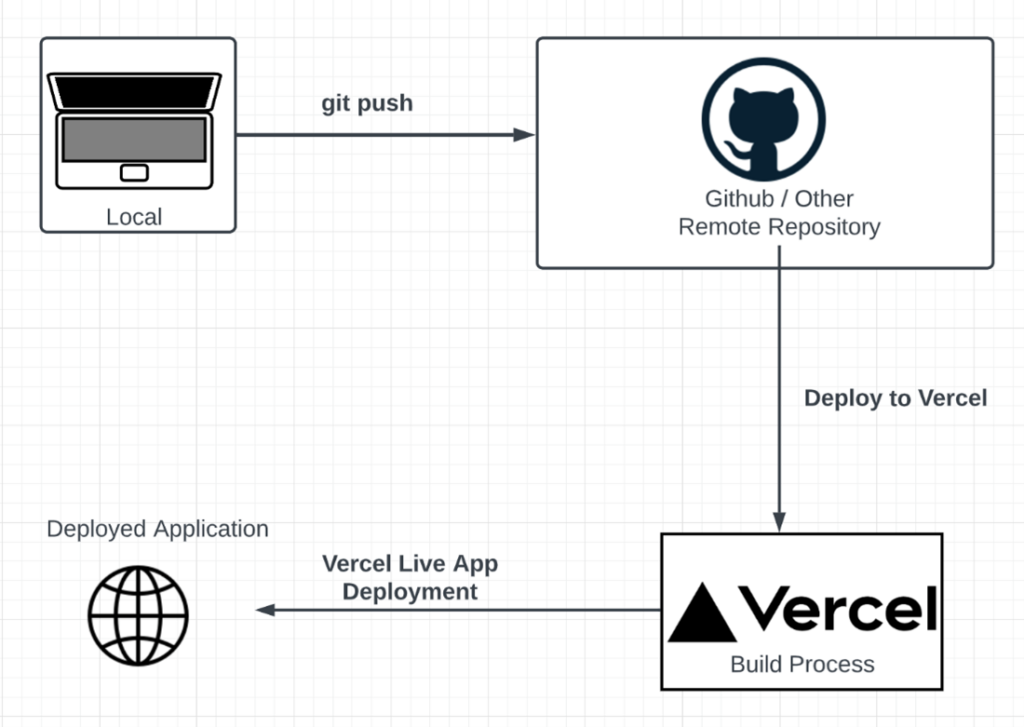
For deployment, I recommend using DigitalOcean or AWS for the backend and Vercel for the frontend. These platforms provide scalability and reliability, ensuring your application can handle increased traffic as it grows.
Conclusion:
Building scalable applications requires careful planning, the right tools, and a focus on user experience. By combining Django and Next.js, you can create powerful, high-performance applications that meet the needs of your users. If you have any questions or need help getting started, feel free to reach out!
